Install Sap On Oracle Rac Administration
Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP workload. 12 minutes to read.In this articleThis document covers several different areas to consider when you're deploying Oracle Database for SAP workload in Azure IaaS. Before you read this document, we recommend you read. We also recommend that you read other guides in the.You can find information about Oracle versions and corresponding OS versions that are supported for running SAP on Oracle on Azure in SAP Note.General information about running SAP Business Suite on Oracle can be found at.Oracle software is supported by Oracle to run on Microsoft Azure. For more information about general support for Windows Hyper-V and Azure, check the.
SAP Notes relevant for Oracle, SAP, and AzureThe following SAP Notes are related to SAP on Azure.
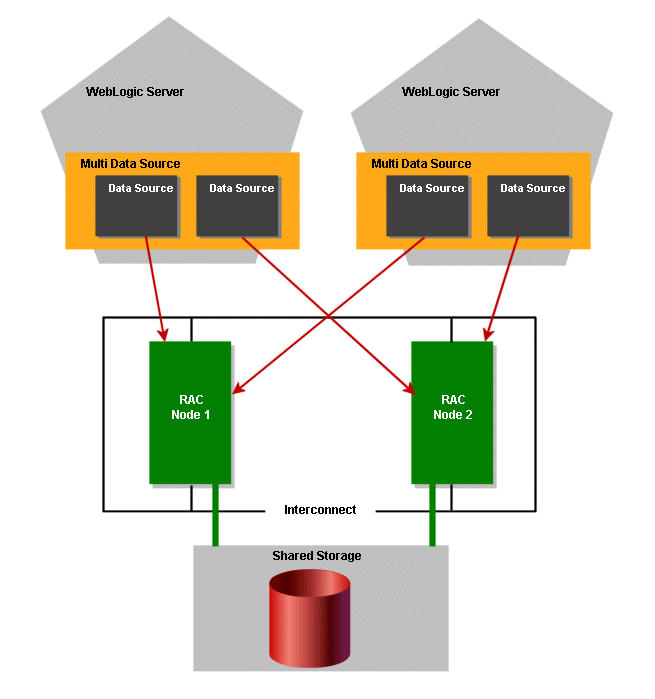
7/15 3 Installing and Configuring Oracle Clusterware and Oracle RACThis chapter explains how to install Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) using Oracle Universal Installer (OUI). You must install Oracle Clusterware before installing Oracle RAC. After your Oracle Clusterware is operational, you can use OUI to install the Oracle Database software with the Oracle RAC components.The example Oracle RAC environment described in this guide uses Oracle Automatic Storage Management (ASM), so this chapter also includes instructions on how to install ASM in its own home directory.This chapter includes the following sections:. Preparing the Oracle Media Installation FileOracle Clusterware is not installed as part of Oracle Database 10 g, but is installed from the Oracle Clusterware installation media.
Because Oracle Clusterware works closely with the operating system, system administrator access is required for some of the installation tasks. In addition, some of the Oracle Clusterware processes must run as the special operating system user, root.The Oracle RAC Database software is installed from the Oracle Database 10 g installation media. By default, the standard Oracle Database 10 g software installation process installs the Oracle RAC option when OUI recognizes that you are performing the installation on a cluster. OUI installs Oracle RAC into a directory structure that is referred to as Oraclehome. This home is separate from the home directories of other Oracle software products installed on the same server.If the Oracle Clusterware installation software and Oracle Database installation software are in ZIP files, create a staging directory on one node, for example, docrac1, to store the unzipped files, as shown here:mkdir -p /stage/oracle/10.2.0Copy the ZIP files to this staging directory. Configuring the Operating System EnvironmentYou run Oracle Universal Installer from the oracle user account.
However, before you start Oracle Universal Installer you must configure the environment of the oracle user. Verifying the Configuration Using the Cluster Verification UtilityIf you have not configured your nodes, network, and operating system correctly, your installation of the Oracle Clusterware or Oracle Database 10g software will not complete successfully.As the oracle user, change directories to the staging directory for the Oracle Clusterware software, or to the mounted installation disk. Then, enter the following command to verify your hardware and operating system setup, where stagingarea is the location of the installation media (for example, /home/oracle/downloads/10gR2/10.2.0 or /dev/dvdrom):oracle $ cd / stagingarea/clusterware/cluvfyoracle $./runcluvfy.sh stage -pre crsinst -n docrac1,docrac2 -verboseThe preceding command instructs the CVU to verify that the system meets all the criteria for an Oracle Clusterware installation. It checks that all the nodes are reachable from the local nodes, proper user equivalence exists, connectivity exists between all the nodes through the public and private interconnects, the user has proper permissions to install the software, and that all system requirements (including kernel version, kernel parameters, memory, swap space, temporary directory space, required software packages) are met.
Note:If you are installing Oracle Clusterware on a server that already has a single-instance Oracle Database 10g installation, then stop the existing ASM instances, if any. After Oracle Clusterware is installed, start up the ASM instances again. When you restart the single-instance Oracle database and then the ASM instances, the ASM instances use the Cluster Synchronization Services Daemon (CSSD) instead of the daemon for the single-instance Oracle database.To install Oracle Clusterware:.Use the following command to start Oracle Universal Installer, where stagingarea is the location of the staging area on disk, or the location of the mounted installation disk:cd / stagingarea/clusterware./runInstaller.The OUI Welcome window appears. Click Next.If you have not installed any Oracle software previously on this server, the Specify Inventory directory and credentials window appears.
The path displayed for the inventory directory should be the oraInventory subdirectory of your Oracle base directory. For example, if you set the ORACLEBASE environment variable to /opt/oracle/10gR2 before starting OUI, then the path displayed is /opt/oracle/10gR2/oraInventory. For the operating system group name, choose oinstall. Click Next.The Specify Home Details window appears. Accept the default value for the Name field, which is the name of the Oracle home directory for this product.
Install Sap On Oracle Rac Administration Login
For the Path field, click Browse to go to and select the directory /opt/oracle/crs, if this path is not already displayed.After you have selected the path, click Next.The next window, Product-Specific Prerequisite Checks, appears after a short period of time. When you see the message 'Check complete. The overall result of this check is: Passed', as shown in the following screen shot, click Next.The Specify Cluster Configuration window appears.Change the default cluster name from crs to a name that is unique throughout your entire enterprise network. For example, you might choose a name that is based on the node names' common prefix.
This guide will use the cluster name docrac.The local node, docrac1, appears in the Cluster Nodes section. If the cluster node names include the domain name, click Edit and remove the domain name from the public, private, and virtual node names. For example, if the node name is docrac1, edit the entries so that they are displayed as docrac1, docrac1-priv, and docrac1-vip. When you have finished removing the domain names in the 'Modify a node in the existing cluster' window, click OK.When you are returned to the Specify Cluster Configuration window, click Add.In the 'Add a new node to the existing cluster' dialog window, enter the second node's public name ( docrac2), private name ( docrac2-priv), and virtual IP name ( docrac2-vip), then click OK.The Specify Cluster Configuration window now displays both nodes in the Cluster Nodes section.Click Next.The Specify Network Interface Usage window appears. Verify eth0 and eth1 are configured correctly (proper subnet and interface type displayed), then click Next.The Specify Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR) Location window appears.Choose Normal Redundancy for the OCR Configuration. You will be prompted for two file locations. In the Specify OCR Location field enter the name of the device configured for the first OCR file.
For example, /dev/raw/raw1. In the Specify OCR Mirror Location field, enter the name of the device configured for the OCR mirror file, for example /dev/raw/raw2.
When finished, click Next. During installation, the OCR data will be written to the specified locations.The Specify Voting Disk Location window appears.Select Normal Redundancy for the voting disk location. You will be prompted for three file locations. For the Voting Disk Location, enter the name of the device configured for the first voting disk file, for example, /dev/raw/raw3. Repeat this process for the other two Voting Disk Location fields. When finished, click Next.The OUI Summary window appears.
Review the contents of the Summary window and then click Install.OUI displays a progress indicator during the installation process.During the installation process, the Execute Configuration Scripts window appears. Do not click OK until you have run the scripts.The Execute Configuration Scripts window shows configuration scripts, and the path where the configuration scripts are located. Run the scripts on all nodes as directed, in the order shown. Note:Do not attempt to run the root.sh script on other nodes. Wait until the script finishes running on the local node.At the completion of this script, the following message is displayed:Local node checking complete.Run root.sh on remaining nodes to start CRS daemons.After the root.sh script finishes on docrac1, go to the terminal window you opened in step c. As the root user on docrac2, enter the following commands:root@docrac2 oraInventory# cd /opt/oracle/crsroot@docrac2 crs#./root.shAfter the root.sh script completes, return to the OUI window where the Installer prompted you to run the orainstRoot.sh and root.sh scripts.
Click OK.The Configuration Assistants window appears. When the configuration assistants finish, OUI displays the End of Installation window. Click Exit to complete the installation process.If you encounter any problems, refer to the configuration log for information. The path to the configuration log is displayed on the Configuration Assistants window. Completing the Oracle Clusterware ConfigurationAfter you have installed Oracle Clusterware, verify that the node applications are running.
Configuring Automatic Storage Management in an ASM Home DirectoryThis section explains how to install the Oracle ASM software in its own home directory. Installing ASM in its own home directory enables you to keep the ASM home separate from the database home directory ( ORACLEHOME). By using separate home directories, you can upgrade and patch ASM and the Oracle Database software independently, and you can deinstall Oracle Database software without affecting the ASM instance.As the oracle user, install ASM by installing the Oracle Database 10 g Release 2 software on the docrac1 node.
Note that the Installer copies the binary files from docrac1 to docrac2 during the installation.To install Oracle ASM in a home directory separate from the home directory used by Oracle Database:.Use the following commands to start OUI, where stagingarea is the location of the staging area on disk, or the location of the mounted installation disk:cd / stagingarea/database./runInstallerWhen you start Oracle Universal Installer, the Welcome window appears. Click Next.The Select Installation Type window appears. Select either Enterprise Edition or Standard Edition and then click Next.In the Specify Home Details window, specify a name for the ASM Home directory, for example, OraASM10ghome. Select a directory that is a subdirectory of your Oracle Base directory, for example, /opt/oracle/10gR2/asm. Click Browse to change the directory in which ASM will be installed.After you have specified the ASM Home directory, click Next.The Specify Hardware Cluster Installation Mode window appears.If your Oracle Clusterware installation was successful, then the Specify Hardware Cluster Installation Mode window lists the nodes that you identified for your cluster, such as docrac1 and docrac2. Click Select All to select all nodes for installation, and then click Next.The Product-Specific Prerequisites Checks window appears.When you see the message 'Check complete. The overall result of this check is: Passed', as shown in the following screenshot, click Next.The Select Configuration Option window opens.Select the Configure Automatic Storage Management (ASM) option to install and configure ASM.
Oracle Rac Training Course
Enter a password for the ASM sys user. Confirm the password by typing it in again in the Confirm ASM SYS Password field.

Then click Next.The Configure Automatic Storage Management window appears.You configure ASM by creating disk groups that become the default location for files created in the database. The disk group type determines how ASM mirrors files. When you create a disk group, indicate whether the disk group is a normal redundancy disk group (2-way mirroring for most files by default), or a high redundancy disk group (3-way mirroring), or an external redundancy disk group (no mirroring by ASM). Use an external redundancy disk group only if your storage system already provides mirroring at the hardware level, or if you have no need for redundant data. The default disk group type is normal redundancy.In the Configure Automatic Storage Management window, the Disk Group Name defaults to DATA.
Enter a new name for the disk group, such as diskgroup1. Check with your system administrator to determine if the disks used by ASM are mirrored at the storage level. If so, select External for the redundancy. If the disks are not mirrored at the storage level, then choose Normal for the redundancy.At the bottom right of the Add Disks section, click Change Disk Discovery Path to select any devices that will be used by ASM but are not listed.In the Change Disk Discovery Path window, enter the path for the devices that ASM will use, such as /dev/sd.
or /dev/raw/raw. Then click OK.You are returned to the Configure Automatic Storage Management window.Select the disks to be used by ASM, for example, /dev/raw/raw5 and /dev/raw/raw8. Then click Next.OUI displays the Summary window. Review the information displayed in this window. If any of the information appears incorrect, then you can click Back to return to a previous window and change it. When you are ready to proceed, click Install.OUI displays a progress window indicating that the installation has started.
The installation takes several minutes to complete. During this time, OUI configures ASM on the specified nodes, and then configures a Listener on those nodes.After ASM has been installed, OUI runs the Configuration Assistants. When the assistants have executed successfully, click the Next button to continue.After the Configuration Assistants have completed their tasks, the Execute Configuration Scripts window appears. You are prompted to run one or more configuration scripts on the specified nodes.You must run the scripts as instructed in the Execute Configuration scripts window before you click OK. For the installation demonstrated in this guide, only one script, root.sh, must be run, and it must be run on both nodes.
The following steps demonstrate how to complete this task on a Linux system (note that for clarity, the examples show the user, node name, and directory in the prompt):.Open a terminal window. As the oracle user on docrac1, change directories to the ASM home directory, and then switch to the root user:oracle@docrac1 oracle$ cd /opt/oracle/10gR2/asmoracle@docrac1 oracle$ su.Enter the password for the root user, and then run the script specified in the Execute Configuration scripts window:root@docrac1 oracle#./root.sh.As the root.sh script runs, it prompts you for the path to the local bin directory. The information displayed in the brackets is the information it has obtained from your system configuration.
Press the Enter key each time you are prompted for input to accept the default choices.After the script has completed, the prompt appears. Verifying Your ASM InstallationVerify that all the database services for ASM are up and running. For example, on the docrac1 node, change directories to the bin directory in the Oracle Clusterware home directory, and then run the following command as the oracle user:cd /opt/oracle/crs/bin./srvctl status asm -n docrac1ASM instance +ASM1 is running on node docrac1.The example output shows that there is one ASM instance running on the local node. Repeat the preceding command, substituting docrac2 for docrac1 to verify the successful installation on the other node in your cluster. Installing the Oracle Database Software and Creating a Cluster DatabaseThe next step is to install the Oracle Database 10 g Release 2 software on the docrac1 node. The installer copies the binary files from docrac1 to docrac2, the other node in the cluster, during the installation process.To install Oracle Database on your cluster:.As the oracle user, use the following commands to start OUI, where stagingarea is the location of the staging area on disk, or the location of the mounted installation disk:cd / stagingarea/database./runInstallerThe OUI Welcome window appears.
Click Next.The Select Installation Type window appears. The Enterprise Edition option is selected by default. Select either Enterprise Edition or Standard Edition and click Next.The Specify Home Details window appears. Specify a name for the Oracle home, for example, OraDb10ghome. You must specify an Oracle home directory. Select a directory that is a subdirectory of your Oracle Base directory, for example, /opt/oracle/10gR2/db1.
Sap Oracle Rac

Click Browse to change the directory in which the Oracle Database software will be installed. After you have selected the directory, click OK.If the directory does not exist, you can type in the directory path in the Directory field, then click OK.
If a window appears asking if you want to create the directory, click Yes.When returned to the Specify Home Details window, verify the information is correct, then click Next.The Specify Hardware Cluster Installation Mode window appears.Select the nodes on which the Oracle Database software will be installed. OUI is cluster-aware and hence knows the other nodes that are in the same cluster as the docrac1 node.Because you are creating a cluster database, select both nodes by clicking Select All. Then click Next.The Product-Specific Prerequisite Checks window appears.In this window, you might see a warning that says the host IP addresses are generated by the dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP), which is not a recommended best practice. You can ignore this warning.When you see the confirmation message that your system has passed the prerequisite checks, click Next.The Select Configuration Option window appears.In the Select Configuration Option window, accept the default option of Create a Database and click Next.The Select Database Configuration window appears.Choose one of the following different types of databases to be created:.General Purpose.Transaction Processing.Data Warehouse.Advanced (for customized database creation)The General Purpose database type is selected by default. Choose the type of database that best suits your business needs. For the example used by this guide, the default value is sufficient. After you have selected the database type, click Next.The Specify Database Configuration Options window appears.Under Database Naming, in the Global Database Name field, enter a fully qualified name for your database, such as sales.mycompany.com.
Ensure that the SID field contains the first part of the database name, for example, sales. Note:The value for the SID will be used as a prefix for the instance names. Thus if the SID is set to sales, the instance names will be sales1, sales2, and so on.Accept the default values for Database Character set (Western European WE8ISO8859P1) or specify a different language, as determined by your business requirements. Select the option Create database with sample schemas if you want sample data and schemas to be created in your database.
After you have made your selections, click Next.The Select Database Management Option window appears.By default, the Use Database Control for Database Management option is selected instead of the Use Grid Control for Database Management option. The examples in this guide use Database Control, which is the default value.Under the option heading Use Database Control for Database Management, do not select the option Enable Email Notifications if your cluster is not connected to a mail server.After you have made your selections, click Next.The Specify Database Storage Option window appears.If you configured ASM on the cluster, select the option Automatic Storage Management (ASM) for the database storage. Otherwise, select the option that you have decided upon for storing the database files, then click Next.The Specify Backup and Recovery Options window appears.Select the default option Do not enable Automated backup, then click Next. You can modify the backup settings at a later time.If you chose ASM as your storage solution, the Select ASM Disk Group window appears.
See Also:or more information on configuring disk groups in ASM.The Select ASM Disk Group window shows you where the database files will be created. Select the disk group diskgroup1 that was created during the ASM installation and then click Next.The Specify Database Schema Passwords window appears.Assign and confirm a password for each of the Oracle database schemas. Unless you are performing a database install action for testing purposes only, do not select the Use the same password for all the accounts option, as this can compromise the security of your data. When finished entering passwords, click Next.OUI displays the Summary window.Review the information displayed in this window. If any of the information is incorrect, click Back to return to a previous window and correct it.
When you are ready to proceed, click Install.OUI displays a progress indicator to show that the installation has begun. This step takes several minutes to complete.As part of the software installation process, the sales database is created.
At the end of the database creation, you will see the Database Configuration Assistant window with the Web address for the Database Control console displayed.Make note of the URL, then click OK and wait for DBCA to start the cluster database and its instances.After the installation, you are prompted to perform the postinstallation task of running the root.sh script on both nodes.On each node, run the scripts listed in the Execute Configuration scripts window before you click OK. Perform the following steps to run the root.sh script:.Open a terminal window. As the oracle user on docrac1, change directories to your Oracle home directory, and then switch to the root user by entering the following commands:oracle@docrac1 oracle$ cd /opt/oracle/10gR2/db1oracle@docrac1 db1$ su.Enter the password for the root user, and then run the script specified in the Execute Configuration scripts window:root@docrac1 db1#./root.sh.As the root.sh script runs, it prompts you for the path to the local bin directory. The information displayed in the brackets is the information it has obtained from your system configuration. Press the Enter key each time you are prompted for input to accept the default choices.After the script has completed, the prompt appears. Open another terminal window, and enter the following commands:oracle@docrac1 oracle$ ssh docrac2oracle@docrac2 oracle$ cd /opt/oracle/10gR2/db1oracle@docrac2 db1$ su.Enter the password for the root user, and then run the script specified in the Execute Configuration scripts window:root@docrac2 db1#./root.sh.Accept all default choices by pressing the Enter key.After you finish executing the script on all nodes, return to the Execute Configuration scripts window and click OK.Click OK on the next window and OUI displays the End of Installation window.
Click Exit and then click Yes to verify that you want to exit. Update the oratab FileSeveral of the Oracle Database utilities use the oratab file to determine the available Oracle homes and instances on each node. The oratab file is created by the root.sh script and is updated by the Database Configuration Assistant when creating or deleting a database.The following is an example of the oratab file:# This file is used by ORACLE utilities. It is created by root.sh# and updated by the Database Configuration Assistant when creating# a database.# A colon, ':', is used as the field terminator.
A new line terminates# the entry. Lines beginning with a pound sign, '#', are comments.## Entries are of the form:# $ORACLESID:$ORACLEHOME::## The first and second fields are the system identifier and home# directory of the database respectively. Reconfigure the User Shell ProfileThere are several environment variables that can be used with Oracle Database. These variables can be set manually in your current operating system session, using shell commands such as set and export.You can also have these variables set automatically when you log in as a specific operating system user. Downloading and Installing RDBMS PatchesPeriodically, Oracle issues bug fixes for its software called patches.
Patch sets are a collection of bug fixes that were produced up to the time of the patch set release. Patch sets are fully tested product fixes. Application of a patch set affects the software residing in your Oracle home only, with no upgrade or change to the database.Ensure that you are running the latest patch set of the installed software.
You might also need to apply patches that are not included in a patch set. Information about downloading and installing patches and patch sets is covered in. Converting an Oracle Database to an Oracle RAC DatabaseYou can optionally use Oracle Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) to convert from a single-instance Oracle database to an Oracle RAC database.
The DBCA automates the configuration of the control file attributes, creates the undo tablespaces and the redo logs, and makes the initialization parameter file entries for cluster-enabled environments. It also configures Oracle Net Services, Oracle Clusterware resources, and Oracle Enterprise Manager.This section contains the following topics:. Installing the Oracle Database 10 g Software with Real Application ClustersAfter you have copied the preconfigured database files to the new node, install the Oracle RAC software on the new node.